Elasticsearch6.3.2启动过程源码阅读记录
网上有很多关于es的源码分析,觉得自己技术深度还不够,所以这些文章只是看源码过程中的一个笔记,谈不上分析。
整个启动过程以类名.方法名,按顺序依次描述如下:
Elasticsearch.main启动入口类,注册JVM关闭钩子用来清理资源。Command.mainwithoutErrorHandling在es正式启动之前,加载一些命令:比如./elasticsearch -help命令
starts elasticsearch Option Description ------ ----------- -EConfigure a setting -V, --version Prints elasticsearch version information and exits -d, --daemonize Starts Elasticsearch in the background -h, --help show help
EnvironmentAwareCommand.execute加载配置参数putSystemPropertyIfSettingIsMissing(settings, "path.data", "es.path.data"); putSystemPropertyIfSettingIsMissing(settings, "path.home", "es.path.home"); putSystemPropertyIfSettingIsMissing(settings, "path.logs", "es.path.logs");
InternalSettingsPrepare.prePareEnvironment解析ElasticSearch.yml中的配置参数Prepares the settings by gathering all elasticsearch system properties, optionally loading the configuration settings,and then replacing all property placeholders.and then replacing all property placeholders.
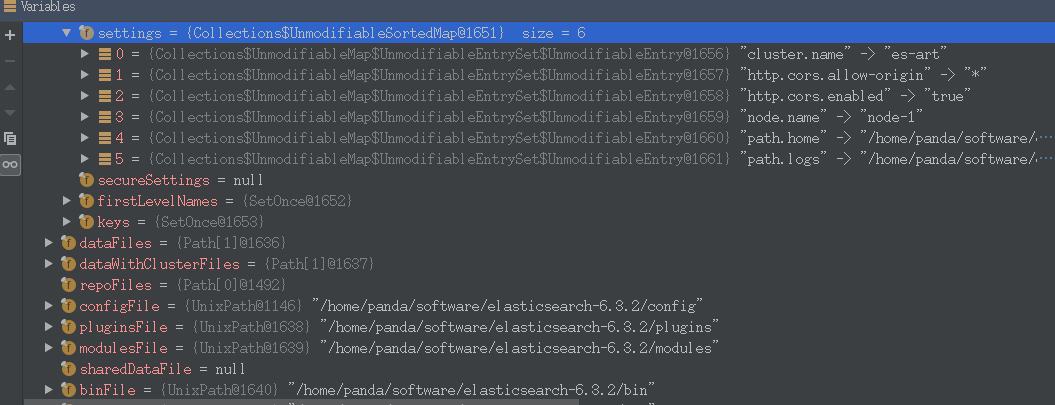
ElasticSearch.execute执行初始化命令。另外在源码中还有看到一些有趣的注释,比如必须设置java.io.tmpdir,这个参数在config/jvm.options文件中指定。// a misconfigured java.io.tmpdir can cause hard-to-diagnose problems later, so reject it immediately try { env.validateTmpFile(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new UserException(ExitCodes.CONFIG, e.getMessage()); }
Bootstrap.init正式开始启动ElasticSearch。This method is invoked by {@link Elasticsearch#main(String[])} to startup elasticsearch。创建节点启动时需要的环境变量参数
final Environment environment = createEnvironment(foreground, pidFile, keystore, initialEnv.settings(), initialEnv.configFile());
checkLucene()检查匹配的Lucene jar包。创建节点,在下面Node构造方法中将详细分析这个过程。
node = new Node(environment) { @Override protected void validateNodeBeforeAcceptingRequests( final BootstrapContext context, final BoundTransportAddress boundTransportAddress, Listchecks) throws NodeValidationException { BootstrapChecks.check(context, boundTransportAddress, checks); } };
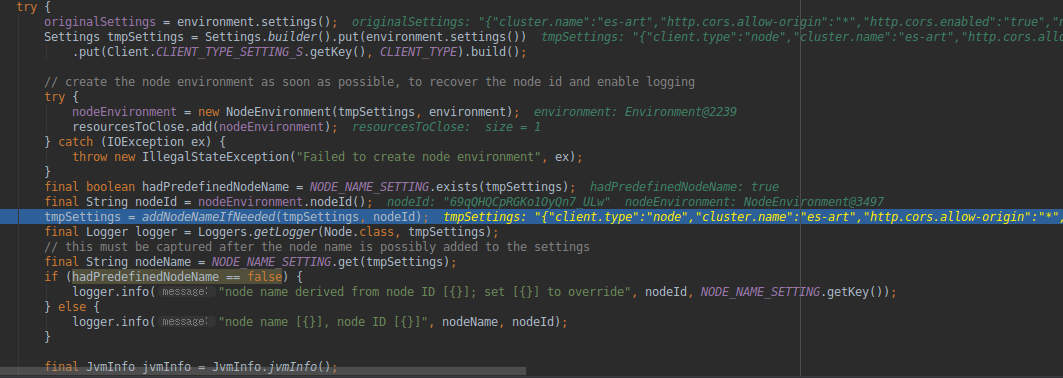
Node.java 构造方法 Node(final Environment environment, Collection<Class<? extends Plugin>> classpathPlugins)。在这个构建方法里面,完成了创建一个节点所需的各种信息,这个方法非常重要,下面就例举出几个节点创建过程中几个重要的流程:- 设置节点环境变量信息(A component that holds all data paths for a single node.)
nodeEnvironment = new NodeEnvironment(tmpSettings, environment);
构造插件服务(PluginService),
this.pluginsService = new PluginsService(tmpSettings, environment.configFile(), environment.modulesFile(), environment.pluginsFile(), classpathPlugins);
看这个构造方法的注释:
/** * Constructs a new PluginService * @param settings The settings of the system * @param modulesDirectory The directory modules exist in, or null if modules should not be loaded from the filesystem * @param pluginsDirectory The directory plugins exist in, or null if plugins should not be loaded from the filesystem * @param classpathPlugins Plugins that exist in the classpath which should be loaded */ public PluginsService(Settings settings, Path configPath, Path modulesDirectory, Path pluginsDirectory, Collection
> classpathPlugins) { 其实就是加载:
elasticsearch-6.3.2/modules和elasticsearch-6.3.2/plugins两个目录下的内容。
创建自定义的线程池,节点执行各种任务用的吧。
final ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(settings, executorBuilders.toArray(new ExecutorBuilder[0]));
创建NodeClient,Client that executes actions on the local node。
client = new NodeClient(settings, threadPool);
AnalysisModule (An internal registry for tokenizer, token filter, char filter and analyzer)各种分词器。
AnalysisModule analysisModule = new AnalysisModule(this.environment, pluginsService.filterPlugins(AnalysisPlugin.class));
SettingsModule(A module that binds the provided settings to the {@link Settings} interface) 各种配置参数用到。比如 jvm.options 和 elasticsearch.yml里面配置的各种参数。
final SettingsModule settingsModule = new SettingsModule(this.settings, additionalSettings, additionalSettingsFilter);
节点是集群的一份子,肯定需要集群相关的服务
final ClusterService clusterService = new ClusterService(settings, settingsModule.getClusterSettings(), threadPool, ClusterModule.getClusterStateCustomSuppliers(clusterPlugins));
集群信息相关服务(Interface for a class used to gather information about a cluster at regular intervals) 周期性同步集群状态。
final ClusterInfoService clusterInfoService = newClusterInfoService(settings, clusterService, threadPool, client, listener::onNewInfo);
创建Module
ModulesBuilder modules = new ModulesBuilder();// plugin modules must be added here, before others or we can get crazy injection errors... for (Module pluginModule : pluginsService.createGuiceModules()) { modules.add(pluginModule); }比如:SearchModule(Sets up things that can be done at search time like queries, aggregations, and suggesters)
SearchModule searchModule = new SearchModule(settings, false, pluginsService.filterPlugins(SearchPlugin.class));
还有 ActionModule(Builds and binds the generic action map, all {@link TransportAction}s, and {@link ActionFilters}.)
ActionModule actionModule = new ActionModule(false, settings, clusterModule.getIndexNameExpressionResolver(), settingsModule.getIndexScopedSettings(), settingsModule.getClusterSettings(), settingsModule.getSettingsFilter(), threadPool, pluginsService.filterPlugins(ActionPlugin.class), client, circuitBreakerService, usageService); modules.add(actionModule);
还有 DiscoveryModule(A module for loading classes for node discovery)
final DiscoveryModule discoveryModule = new DiscoveryModule(this.settings, threadPool, transportService, namedWriteableRegistry, networkService, clusterService.getMasterService(), clusterService.getClusterApplierService(), clusterService.getClusterSettings(), pluginsService.filterPlugins(DiscoveryPlugin.class), clusterModule.getAllocationService());
看一下,一共都有哪些module:
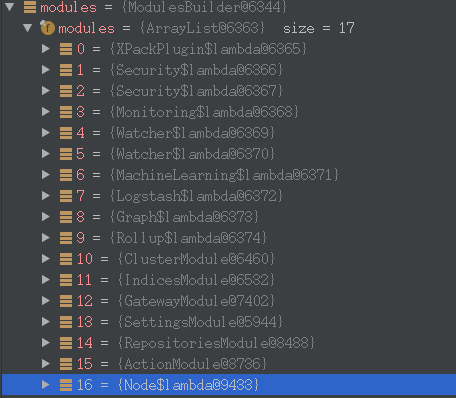
最终关联了一大批的Module
modules.add(b -> { b.bind(Node.class).toInstance(this); b.bind(NodeService.class).toInstance(nodeService); b.bind(NamedXContentRegistry.class).toInstance(xContentRegistry); b.bind(PluginsService.class).toInstance(pluginsService); b.bind(Client.class).toInstance(client); b.bind(NodeClient.class).toInstance(client); b.bind(Environment.class).toInstance(this.environment); b.bind(ThreadPool.class).toInstance(threadPool); b.bind(NodeEnvironment.class).toInstance(nodeEnvironment); b.bind(ResourceWatcherService.class).toInstance(resourceWatcherService); b.bind(CircuitBreakerService.class).toInstance(circuitBreakerService); b.bind(BigArrays.class).toInstance(bigArrays); b.bind(ScriptService.class).toInstance(scriptModule.getScriptService()); b.bind(AnalysisRegistry.class).toInstance(analysisModule.getAnalysisRegistry()); b.bind(IngestService.class).toInstance(ingestService); b.bind(UsageService.class).toInstance(usageService); b.bind(NamedWriteableRegistry.class).toInstance(namedWriteableRegistry); b.bind(MetaDataUpgrader.class).toInstance(metaDataUpgrader); b.bind(MetaStateService.class).toInstance(metaStateService); b.bind(IndicesService.class).toInstance(indicesService); b.bind(SearchService.class).toInstance(searchService); b.bind(SearchTransportService.class).toInstance(searchTransportService); b.bind(SearchPhaseController.class).toInstance(new SearchPhaseController(settings, searchService::createReduceContext)); b.bind(Transport.class).toInstance(transport); b.bind(TransportService.class).toInstance(transportService); b.bind(NetworkService.class).toInstance(networkService); b.bind(UpdateHelper.class).toInstance(new UpdateHelper(settings, scriptModule.getScriptService())); b.bind(MetaDataIndexUpgradeService.class).toInstance(metaDataIndexUpgradeService); b.bind(ClusterInfoService.class).toInstance(clusterInfoService); b.bind(GatewayMetaState.class).toInstance(gatewayMetaState); b.bind(Discovery.class).toInstance(discoveryModule.getDiscovery());
总之,Node.java的构造方法里面实现了创建一个ElasticSearch节点所必须的各种信息,想要了解ElasticSearch节点的内部结构,应该就得多看看这个方法里面的代码吧。
ModulesBuilder.createInjector使用了Guice 依赖注入。injector = modules.createInjector();
Node.start,前面创建了节点,现在开始启动节点。(Start the node. If the node is already started, this method is no-op)先拿到对象实例,再启动
injector.getInstance(MappingUpdatedAction.class).setClient(client); injector.getInstance(IndicesService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(IndicesClusterStateService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(SnapshotsService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(SnapshotShardsService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(RoutingService.class).start(); injector.getInstance(SearchService.class).start(); nodeService.getMonitorService().start();//... Discovery discovery = injector.getInstance(Discovery.class); clusterService.getMasterService().setClusterStatePublisher(discovery::publish); discovery.start(); // start before cluster service so that it can set initial state on ClusterApplierService clusterService.start();
里面的每个方法,都值得花时间去深入研究下。哈哈。。。
总结
总的来看,Elasticsearch启动过程三大步,第一步:加载各种配置信息,这些配置信息既有自定义的配置信息,也有机器的环境变量信息,它们告诉es,我想要创建一个什么样的节点。第二步:创建节点,节点具有各种各样的功能,比如说执行搜索查询请求、选主、与其他节点同步集群状态信息……这些功能需要各种服务/插件/模块Module来实现。第三步:启动节点,其实就是各种模块、插件、服务的启动。
最后放一张整理上上面的9个方法的调用关系图: 
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/hapjin/p/10124269.html